A measured building survey is the process of precisely measuring a building’s dimensions, layout, and structural features to create accurate technical drawings or 3D models. Conducted by professional surveyors, it provides the essential “building block” of information needed for various construction, renovation, and design projects

Uses for a measured building survey
This type of survey is an essential first step for many types of building projects, ensuring that architects and designers have reliable information to base their plans on. Common uses include:
- Planning an extension or renovation: Provides architects with accurate layouts to design a new addition that integrates correctly with the existing structure.
- Property redevelopment or refurbishment: Offers a detailed record of the existing building, which is necessary for major structural changes.
- Legal documentation: Supplies precise floor area calculations, such as Net Internal Area (NIA), for lease plans, land registry, or property transactions.
- Historic building preservation: Creates a detailed record of a building’s features for restoration projects.
- Space planning: Helps landlords and businesses plan new internal layouts, especially for commercial properties.
- To reduce risk: Ensures that any work is based on reliable data, minimizing errors and unforeseen issues.
What our Measured Building Survey can include
Depending on the project’s requirements, a measured building survey can include some or all of the following deliverables:
- Floor plans: Detailed plan views showing the layout and dimensions of each floor, including walls, doors, and windows.
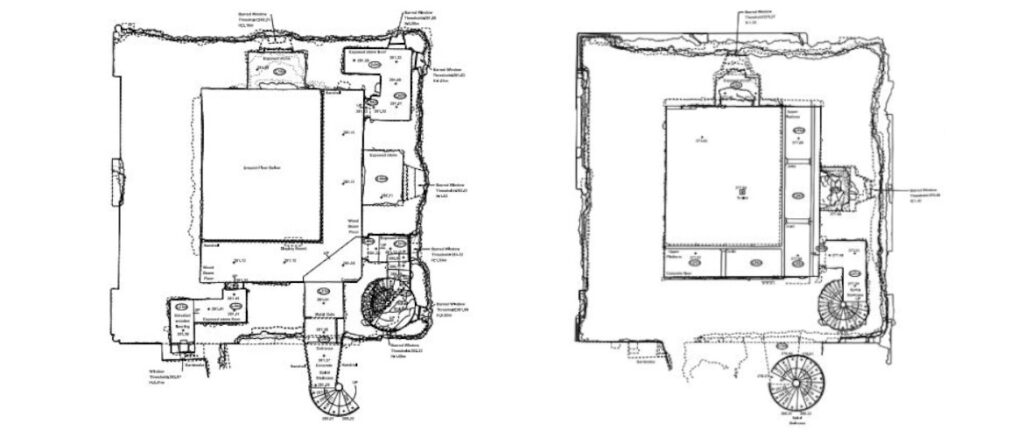
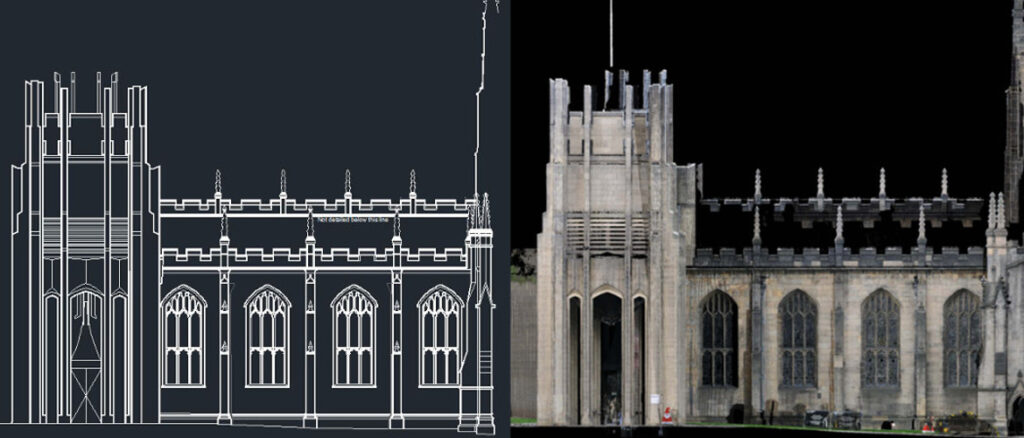
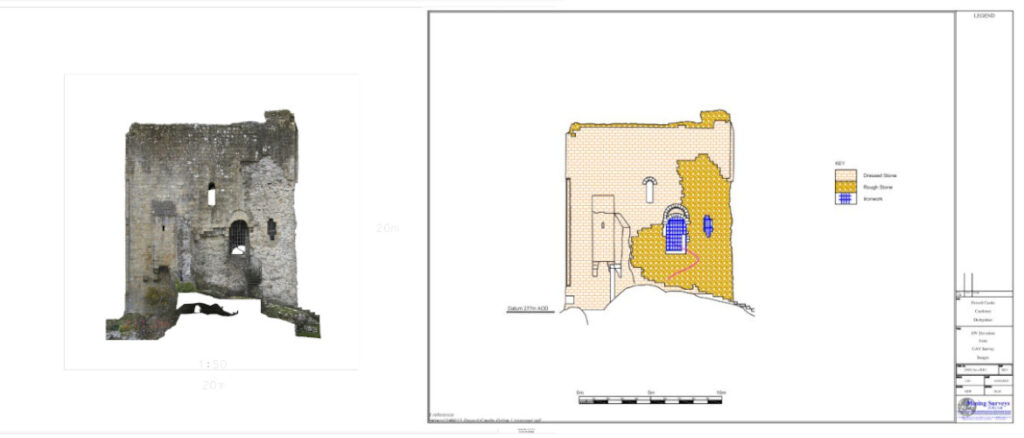
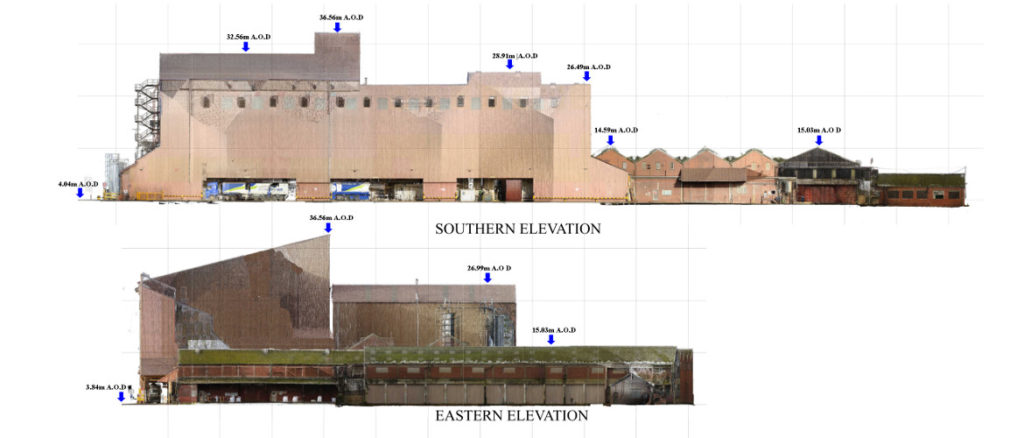
- External elevations: Scaled drawings showing the detail on each of the external sides of the building.
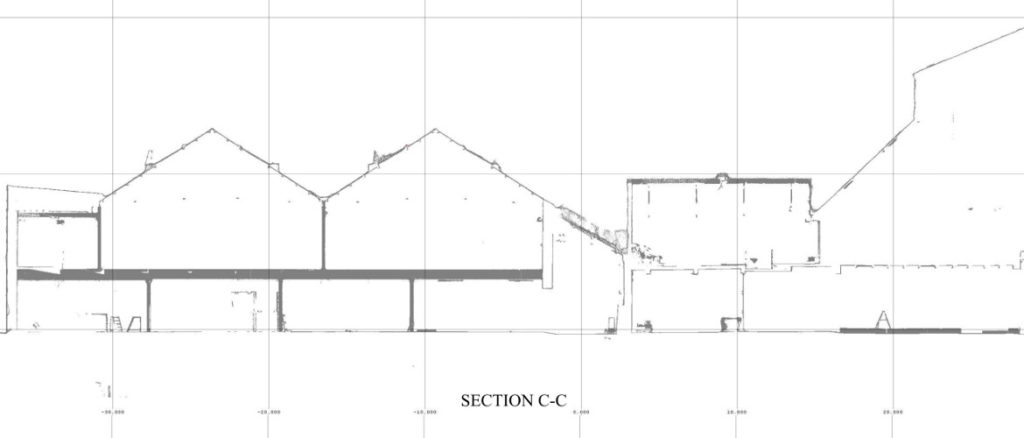
- Cross-sections: A view that “slices” through the building to show the internal structure, floor and ceiling heights, and relationships between different levels.
- Roof plans: A plan view detailing the shape, slope, and features of the roof.

- 3D models: Created from laser-scan data, or photogrammetry, these models, often in BIM-ready formats like Revit, but also in more detailed and photo-realistic formats, provide a complete, interactive, three-dimensional digital replica of the building.
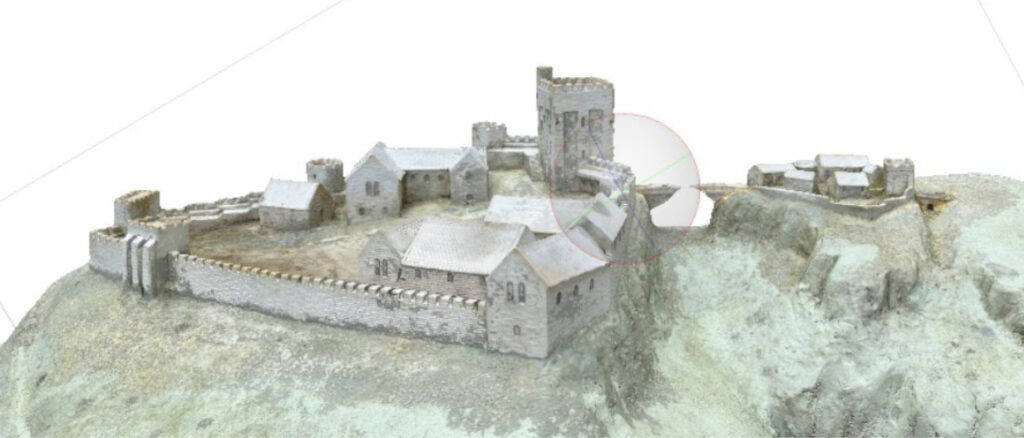

- Point clouds: The raw data from a 3D laser scan, which consists of millions of individual measurement points that can be used to generate drawings and models.
How our surveys are conducted
Our surveyors combine traditional and modern methods to ensure the highest degree of accuracy:
- 3D laser scanners: These devices capture millions of data points to create a detailed “point cloud,” which forms the basis for 2D drawings and 3D models.
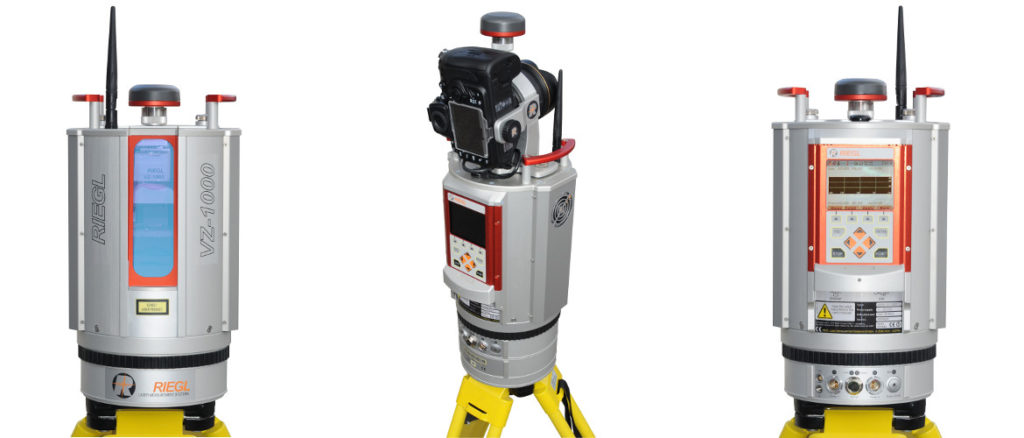

- Total stations: Highly precise electronic instruments used to measure distances and angles.
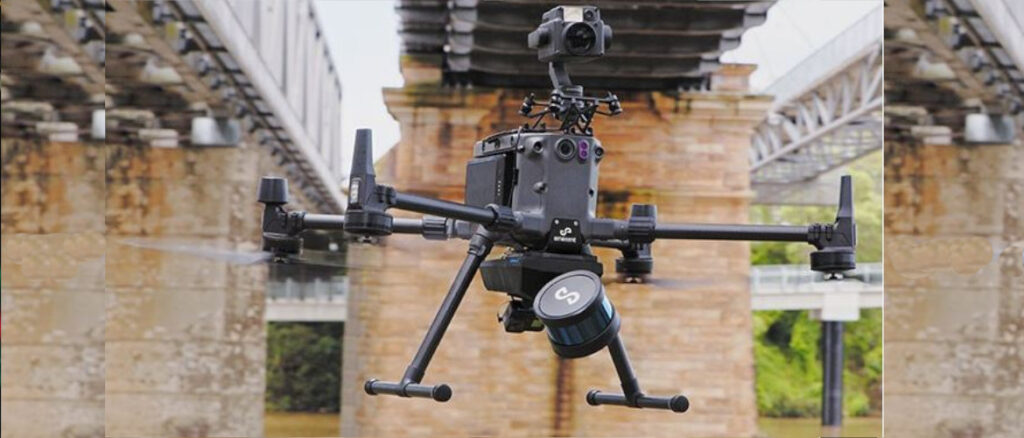
- Survey Grade Drones: Employed for capturing aerial imagery and measurements, usually LiDAR scans, for hard-to-reach areas like roofs.

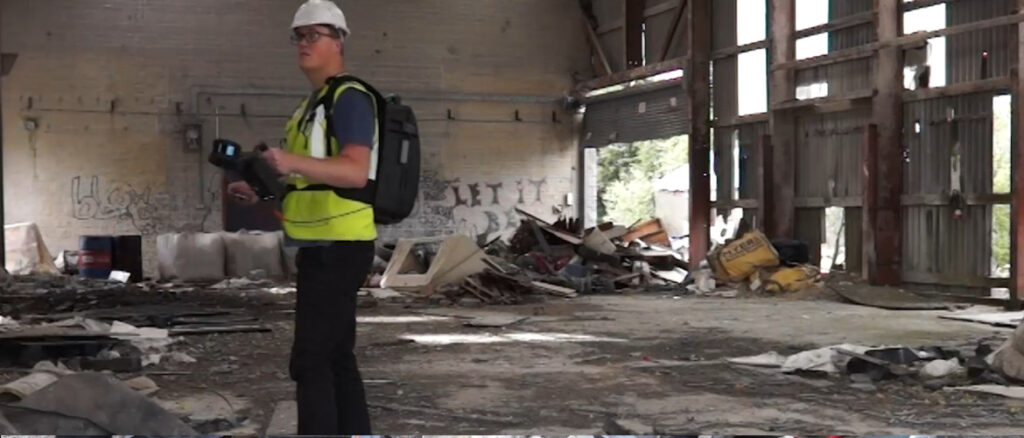
- Hand Held Scanners: For small or hard to reach areas help provide a complete 3D model of the building or structure

- Manual measurements: Basic tools like tape measures are still used for smaller details or in areas that are not accessible with modern equipment.
Choosing a survey specification
The specific type and level of detail required for a survey depend on the scope and needs of the project. For example, a minor home extension may only require basic floor plans, while a major redevelopment or a heritage building restoration would require a full 3D model with intricate detail. Our surveyors will work with clients to tailor the survey to their exact needs.
