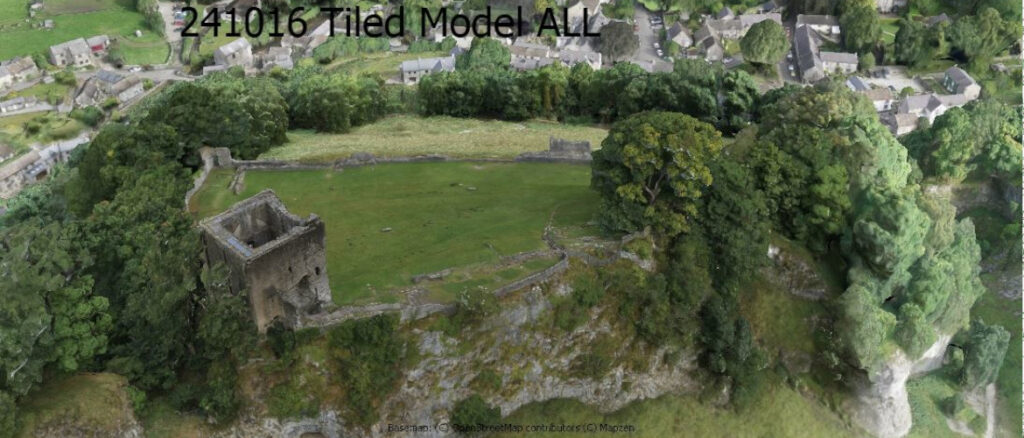
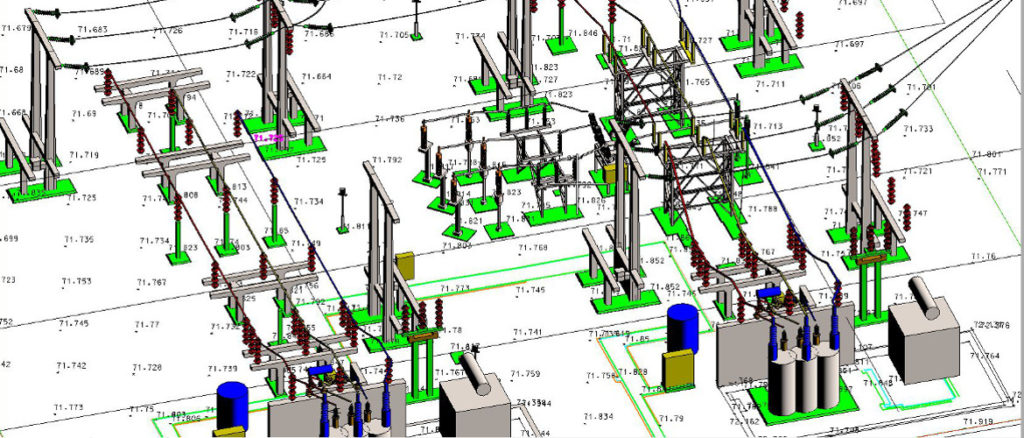
Reality capture is the process of digitally documenting a physical environment to create an accurate 3D model, such as a point cloud or mesh. This is achieved using technologies like laser scanning or photogrammetry (using photographs) and can be used for applications in construction, architecture, and surveying to document existing conditions, monitor projects, and create digital twin.
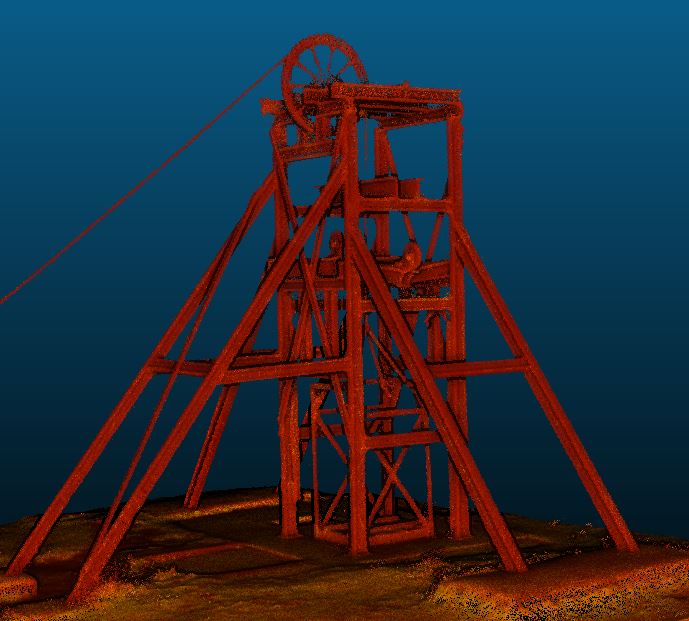
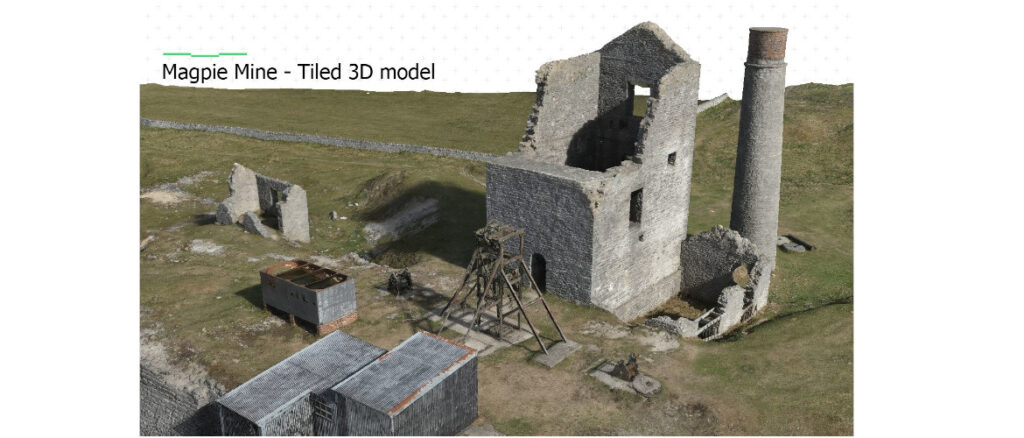
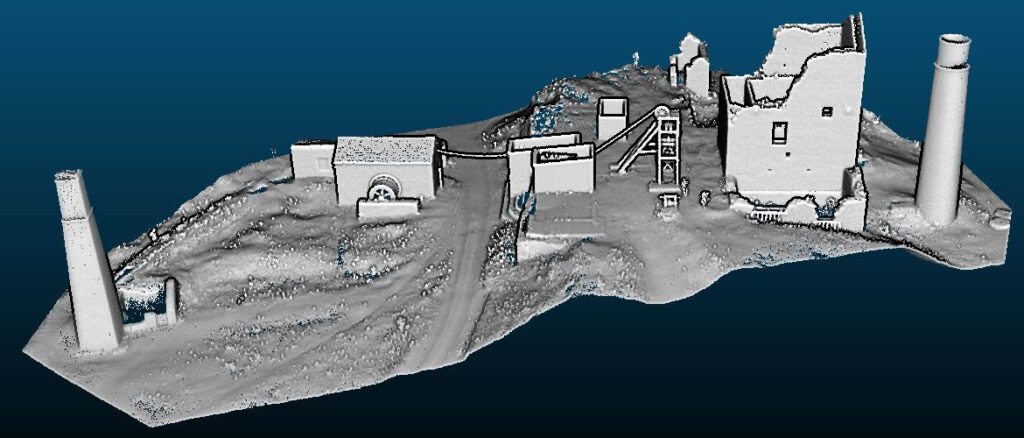

How it works
- Scanning:Technologies like laser scanners or LiDAR are used to capture precise measurements of a physical space, creating a dense “point cloud” of data in three-dimensional space.
- Photogrammetry:This method uses a series of overlapping photographs, often taken from the ground or a drone, to reconstruct a 3D model with realistic textures.
- Data processing:The raw data from scanning or photography is processed using software to create a final, usable 3D model or digital twin.
How it’s used
- Construction and design:It helps in accurately modeling existing buildings for renovation or new construction projects, allowing for precise design and comparison with as-built models.
- Quality control:Teams can remotely inspect project sites using visual data captured through reality capture, which is particularly useful for monitoring progress and identifying safety hazards.
- Documentation:It provides a detailed, high-resolution record of a site at a specific moment in time, which is useful for everything from historic preservation to forensic work.
- Asset management:Creating a digital model or “digital twin” allows for better management of an entire building or facility.
Common applications
- Construction: Monitoring progress, comparing “as-built” conditions to design plans, and documenting sites for quality control.
- Architecture and engineering: Accurately measuring existing buildings and sites to inform design and renovation projects.
- Cultural heritage: Digitally preserving historical sites and artifacts for future study and archiving.
- Utilities and infrastructure: Inspecting and monitoring complex facilities like power plants and railways.
- Public safety: Reconstructing crime scenes and accidents with millimeter-level accuracy for forensic analysis.
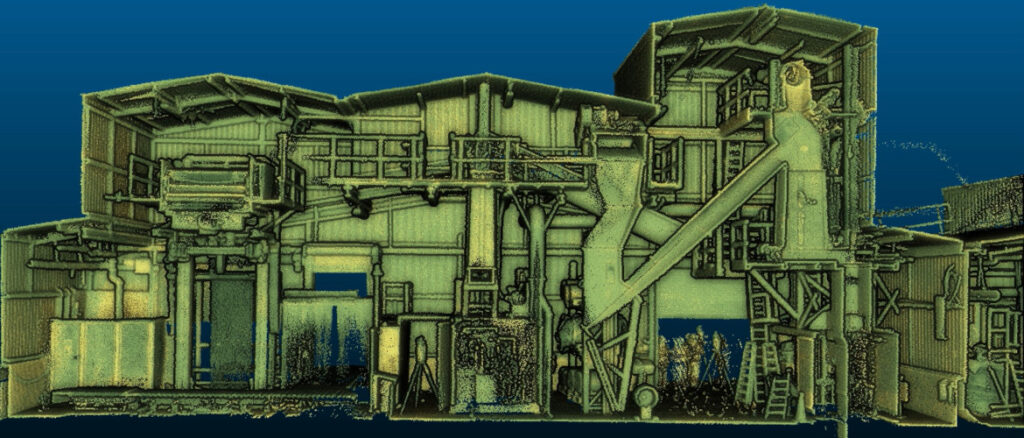
Core technologies
Reality capture relies on several different technologies, which can be used individually or combined to create a digital model:
- 3D Laser Scanning / LiDAR: High-precision scanners that use laser pulses to collect millions of measurements and create a “point cloud”—a dense dataset of 3D points. This method is highly accurate and ideal for detailed measurements.
- Photogrammetry: Software that processes a series of overlapping, high-resolution photographs to generate detailed 3D models. Drones or standard cameras can be used for capture.
- 360-degree cameras: These capture immersive, panoramic views of a space, enabling virtual walkthroughs for remote viewing and documentation.
- Mobile mapping: Handheld or vehicle-mounted scanners that use a combination of sensors to capture large areas quickly and efficiently.
Benefits of reality capture
- Enhanced accuracy and precision: Digital models offer a near-perfect reflection of physical environments, which eliminates human error associated with manual measurements.
- Time and cost efficiency: Capturing large amounts of data is much faster than traditional surveying methods, which can reduce on-site labor and travel time. This saves money and helps avoid expensive rework.
- Improved collaboration: Digital twins provide a single, centralized “source of truth” that all project stakeholders can access from anywhere. This improves communication and reduces misunderstandings.
- Increased safety: Teams can use digital models to identify potential hazards and create safer working procedures, especially in dangerous or inaccessible environments.
- Detailed documentation: For historic preservation, construction, or maintenance, reality capture creates a rich, permanent record of a project’s state at any point in time.